이 문서는 SpringBoot2.0 의 기본인 Junit4 대신에 Junit5를 적용해보면서 정리해봅니다. (기준 버전 junit 5.5.1, SpringBoot 2.0 버전)
공식 문서의 축약 버전입니다.
참고. SpringBoot 2.2.0 버전에서는 junit5 에서는 기본으로 변경됨.
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.2-Release-Notes#junit-5
JUnit5 ?
JUnit 5은 기존버전과 다르게 3개의 sub-project로 이뤄져있다.
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform : JVM 기반 테스팅 프레임워크를 실행시키기 위한 기반 모듈. Launcher and TestEngine APIs.
JUnit Jupiter : Junit5를 테스트하고 확장 모델을 지원하기 위한 모듈
JUnit Vintage : JUnit3와 JUnit4 기반의 테스트를 JUnit Platform에서 실행시키기 위한 TestEngine을 제공하는 모듈
지원하는 자바 버전
Junit5는 런타임시 Java8(또는 그 이상)을 필요로 하고, 하위 버전의 jdk로도 컴파일은 가능하다.
SpringBoot2에 JUnit적용하기
SpringBoot 2.2.0 버전에서는 junit5 에서는 기본으로 변경됨.
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.2-Release-Notes#junit-5
SpringBoot 2.2.0 이전 버전에서의 junit5 설정
junit-platform-engine과 junit-platform-commons 라이브러리를 추가로 지정했는데 그 원인은 여기를 참고.
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') {
exclude module: 'junit'
}
testImplementation("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.5.1") {
exclude module:'junit-platform-commons'
}
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.5.1")
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.platform:junit-platform-engine:1.5.1")
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.platform:junit-platform-commons:1.5.1")
@DisplayName
기존에 method명으로 표현하기 부족했던 테스트명을 따로 정할 수 있다. 클래스와 메소드에 붙일 수 있다.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@DisplayName("A special test case")
class DisplayNameDemo {
@Test
@DisplayName("Custom test name containing spaces")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpaces() {
}
@Test
@DisplayName("╯°□°)╯")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpecialCharacters() {
}
}
테스트명을 한글, 띄어쓰기가 있는 엄청 긴 이름, 특수문자나 이모지도 넣기가 가능. 위의 코드를 테스트를 수행하면 이렇게 표현이 된다.
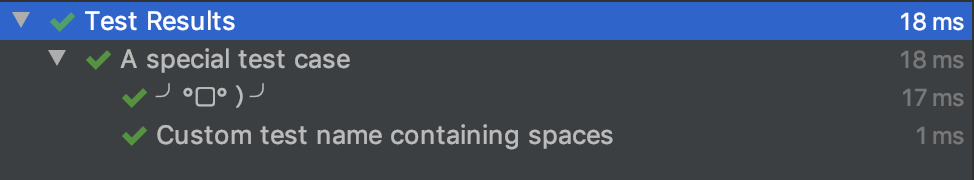
@Disabled
기존 버전의 @Ignore("blah") 어노테이션은 @Disabled("blah")로 변경.
Lifecycle Method
- 기존 버전과 같고 Annotation만 변경됨.
- @BeforeClass, @AfterClass -> @BeforeAll, @AfterAll
- @Before, @After -> @BeforeEach, @AfterEach
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.fail;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class StandardTests {
@BeforeAll
static void initAll() {
}
@BeforeEach
void init() {
}
@Test
void succeedingTest() {
}
@Test
void failingTest() {
fail("a failing test");
}
@Test
@Disabled("for demonstration purposes")
void skippedTest() {
// not executed
}
@Test
void abortedTest() {
assumeTrue("abc".contains("Z"));
fail("test should have been aborted");
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
}
@AfterAll
static void tearDownAll() {
}
}Assertions
람다 구문을 쓸 수 있다.
class AssertionsDemo {
private final Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
private final Person person = new Person("Jane", "Doe");
@Test
void standardAssertions() {
assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1));
assertEquals(4, calculator.multiply(2, 2),
"The optional failure message is now the last parameter");
assertTrue('a' < 'b', () -> "Assertion messages can be lazily evaluated -- "
+ "to avoid constructing complex messages unnecessarily.");
}
@Test
void groupedAssertions() {
// In a grouped assertion all assertions are executed, and all
// failures will be reported together.
assertAll("person",
() -> assertEquals("Jane", person.getFirstName()),
() -> assertEquals("Doe", person.getLastName())
);
}
@Test
void dependentAssertions() {
// Within a code block, if an assertion fails the
// subsequent code in the same block will be skipped.
assertAll("properties",
() -> {
String firstName = person.getFirstName();
assertNotNull(firstName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("first name",
() -> assertTrue(firstName.startsWith("J")),
() -> assertTrue(firstName.endsWith("e"))
);
},
() -> {
// Grouped assertion, so processed independently
// of results of first name assertions.
String lastName = person.getLastName();
assertNotNull(lastName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("last name",
() -> assertTrue(lastName.startsWith("D")),
() -> assertTrue(lastName.endsWith("e"))
);
}
);
}
}
@ParameterizedTest
한 메소드에 여러 파라미터 값을 다르게 넣어서 테스트하기
@ParameterizedTest 을 쓰기 위해서는 dependency를 따로 추가해 주어야 한다.
testCompile('org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-params:5.5.1')
@DisplayName("여러 seq로 조회")
@ParameterizedTest(name = "seq {0} 조회")
@ValueSource(longs = { 1L, 2L })
void getBySeq(Long seq) {
Review review = reviewService.getByReviewSeq(seq);
assertThat(review).isNotNull();
}더 자세히: https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests-parameterized-tests
JUnit 5 User Guide
Although the JUnit Jupiter programming model and extension model will not support JUnit 4 features such as Rules and Runners natively, it is not expected that source code maintainers will need to update all of their existing tests, test extensions, and cus
junit.org
@RepeatedTest
여러번 반복하고 싶다면?
@RepeatedTest(10)
void repeatedTest() {
// ...
}
@Nested - 중첩된 테스트 클래스
유사한 성격의 테스트들을 클래스로 묶어서 표현이 가능하다. 개발자가 보기 쉽게.
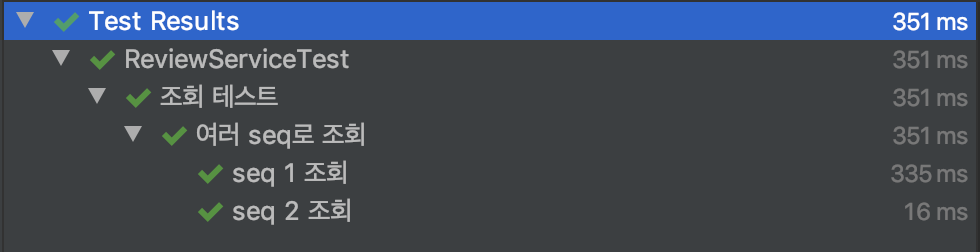
@DisplayName("조회 테스트")
@Nested
class ReadTest {
@DisplayName("여러 seq로 조회")
@ParameterizedTest(name = "seq {0} 조회")
@ValueSource(longs = { 1L, 2L })
void getBySeq(Long seq) {
Review review = reviewService.getByReviewSeq(seq);
assertThat(review).isNotNull();
}
}
결과:
Nested 클래스일때 LifeCycle
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
class NestedTest {
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("Parent beforeAll");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("Parent beforeEach");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("Parent afterEach");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("Parent afterAll");
}
@Test
void test() {
System.out.println("Parent test");
}
@Nested
class Child {
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("Child beforeEach");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("Child afterEach");
}
@Test
void test() {
System.out.println("Child Test");
}
}
}
결과:
|
Parent beforeAll Parent beforeEach
Parent afterAll |
Nested 클래스 안에서는 @BeforeAll 이나 @AfterAll 메서드를 사용할 수 없다.
Java는 Nested 클래스 내에서 static 메서드를 허용하지 않기 때문.
단 부모 클래스의 생명주기를 @TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS) 사용 시에는 @BeforeAll 과 @AfterAll을 사용할 수 있다.
Test Instance Lifecycle
자세히: https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests-test-instance-lifecycle
Test Instance의 기본값은 TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_METHOD 모드이다.
기존 Junit 버전에서 썼던 것처럼 test instance는 각 test method, test factory method, test template method 마다 실행된다.
Junit5에선 @TestInstance를 TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS 모드가 추가되었다.
test instance는 test class 당 하나가 생긴다.
이 모드를 사용하면 @BeforeAll, @AfterAll 을 붙인 메소드가 static 일 필요가 없다.
Junit5 이전 버전에서 @BeforeClass에 해당하는 메소드는 static으로 선언해야 했다. 하지만 Junit5 에선 static일 필요가 없다.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional
@Rollback
@TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)
public class ReviewServiceTest {
....
@BeforeAll
void setUp() {
review = Review.builder()
.userId("userId")
.subject("subject")
.contents("contents")
.rating(5)
.build();
reviewService.saveReview(review);
}
한줄평
JUnit5의 @DisplayName, @Nested 클래스, @ParameterizedTest, 람다 지원만으로도 충분히 갈아탈만 하다.
'backend > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] WebClient DataBufferLimitException WebFlux 오류 해결 (0) | 2022.04.10 |
|---|---|
| [SpringData JPA] query method predicate keywords - null이 아닌 빈값을 제외하고 싶을때 (0) | 2021.10.14 |
| [Junit5] SpringBoot2+Junit5 에서 TestEngine with ID 'junit-jupiter' failed to discover tests 오류 해결방법 (3) | 2019.07.26 |
| [Spring] Lazy Initialization in Spring Boot 2.2 - 번역 (0) | 2019.07.16 |
| [SpringSecurity] Authentication(인증) 관련 클래스와 처리 (0) | 2016.01.25 |
| [Spring] @Autowired의 Before/After (2) | 2009.04.29 |
| [Spring] 스프링에서 VelocityTools 환경설정 (2) | 2008.03.20 |
| [Spring] 스프링 MVC를 이용한 웹 요청 처리 (4) | 2008.03.13 |